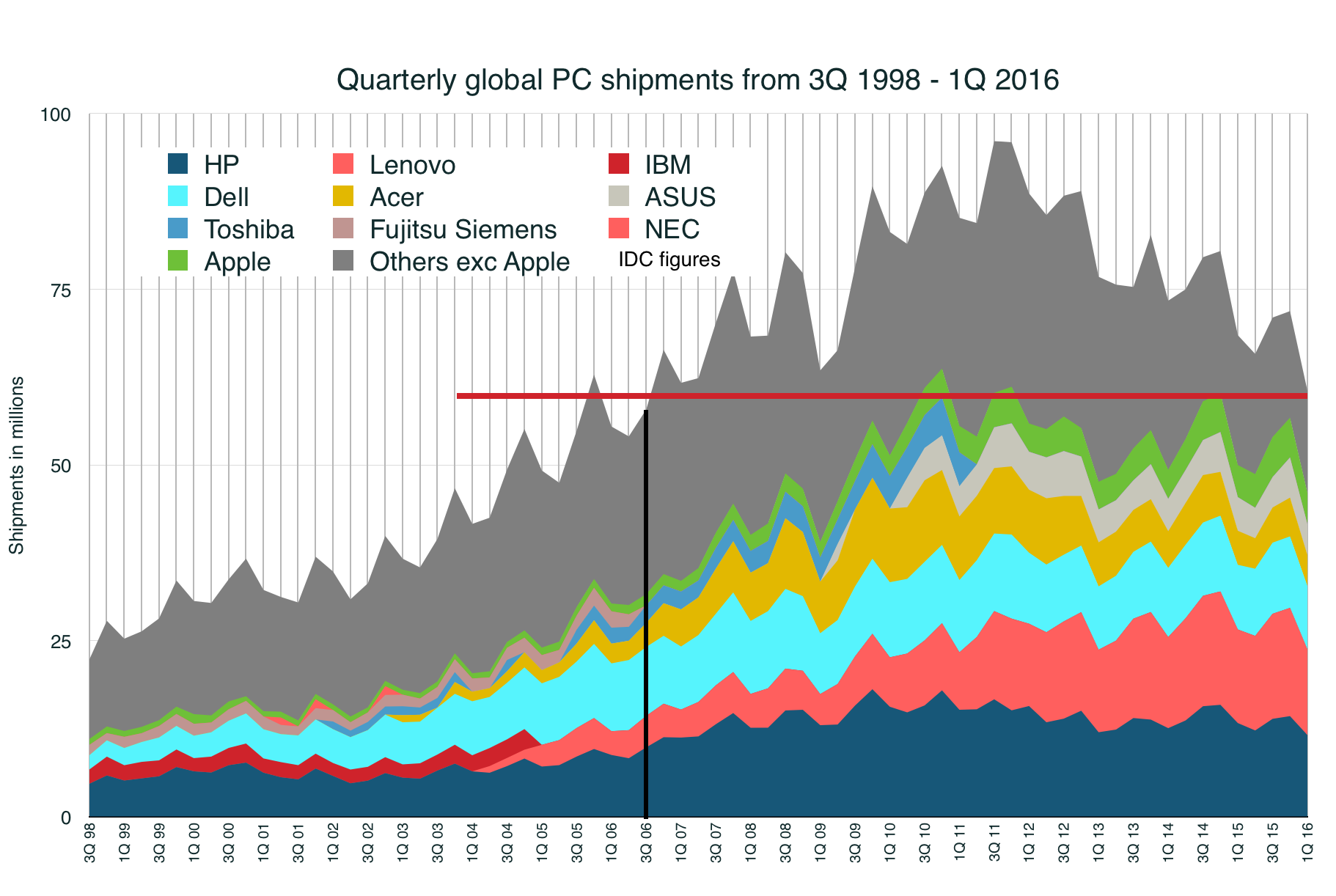
The PC industry isn’t getting any healthier. Both IDC’s and Gartner’s figures for PC shipments in the first quarter are out and both show the same direction of travel: down 11.5% to 60.6m units for IDC, down 9.6% to 64.8m units for Gartner.
There are some variations between what the two count as a “PC”: IDC doesn’t include Windows tablets, 2-in-1s such as the Lenovo Yoga, but does include Chromebooks; Gartner doesn’t include Chromebooks, but does include 2-in-1s and Windows tablets. (You might think comparing the two datasets would make it easy to spot who is doing well in Chromebooks, and who isn’t doing well in 2-in-1s or Windows tablets. Sadly, that turns out not to be true; but we can say Chromebooks account for only a few million sales per year and there aren’t any clear signs of that changing.)
At the moment, PC shipments have receded below the point they were at in 3Q 2006 (by IDC’s data); that’s nearly a decade of progress wiped out. It’s a category in retreat. The peak was in 3Q 2011, at 96.1m (IDC) or 95.4m (Gartner).
There are a few points to note in what’s going on.
The Long Slow Goodbye
First, Windows PCs are in serious long-term decline, more so than Apple. Once you subtract Apple’s contribution, you find Windows shipments have been in a year-on-year decline for 15 straight quarters. That’s nearly four years.
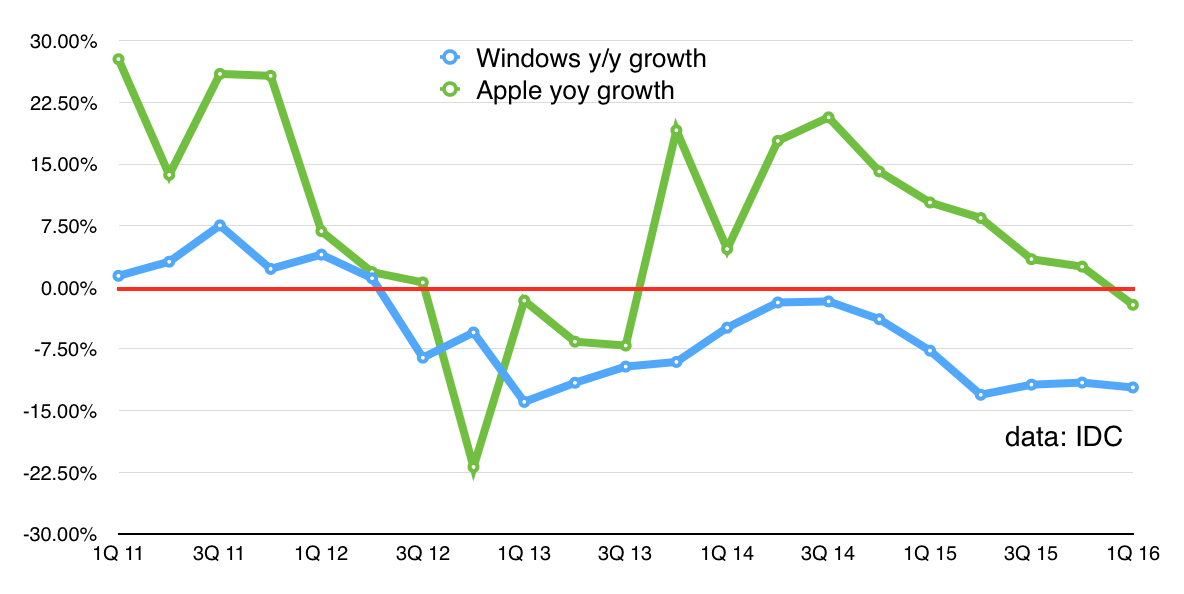
Something Happened
Second, the trigger for that decline is entirely unlike the trigger for previous declines in PC shipments. If you look at the long-term view, there are three points since 1999 when Windows PC shipments have shrunk: near the end of 2001 (during a worldwide recession), the end of 2008 (during the global financial crash), and towards the end of 2012.
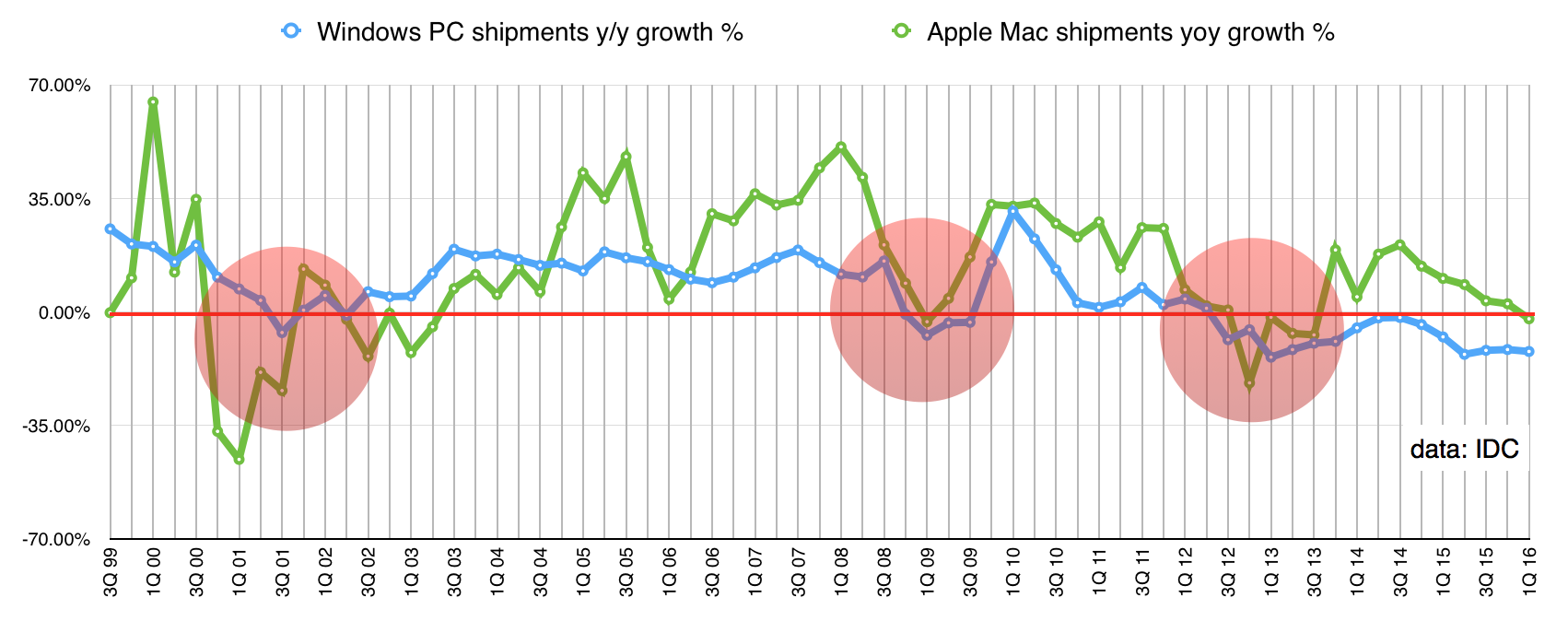
What happened in 2012? Nothing external. Instead, the decline seems to have been prompted by the twin thrust of tablets and smartphones. Tablets became broadly available (the iPad 2 dropped in price) and smartphone screens grew larger (the first Samsung Galaxy Note, with a 5.3in screen, had been launched at the end of 2011, and the Note 2 was coming along).
Ben Thompson, writing at Stratechery ($subscription), suggests PCs are being disrupted. What we’re seeing is “less capable” and cheaper devices (tablets and smartphones) taking over the jobs that were being done by much more capable devices. But the users didn’t generally need that capability; browsing, email, writing text, organising and uploading photos and watching video, plus a few games, tended to fill the gamut of what most people need to do on a computer.
Certainly, all the signs are that Thompson is right. That 2012 decline points strongly to a change and, at Gartner, Mikako Kitagawa says, “The ongoing decline in US PC shipments showed that the installed base is still shrinking, a factor that played across developed economies.” A shrinking PC installed base? That must be quite a worry. But it’s what we’re seeing.
Linn Huang of IDC offers something of a hostage to fortune: “The PC market should experience a modest rebound in the coming months.”
The Others
Third, anyone in the “Other” category is probably getting pretty worried now. Even Acer has fallen out of the top five computer makers, displaced by Apple. (I continue to include it, estimating its volumes as slightly below Apple’s.)
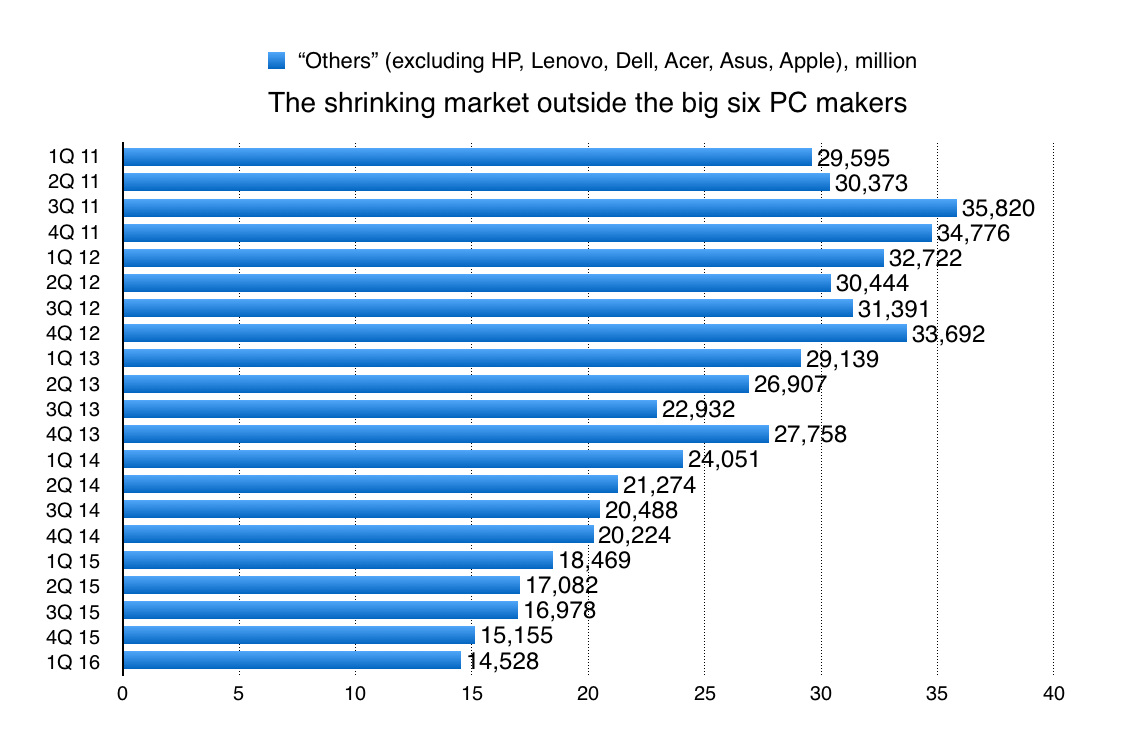
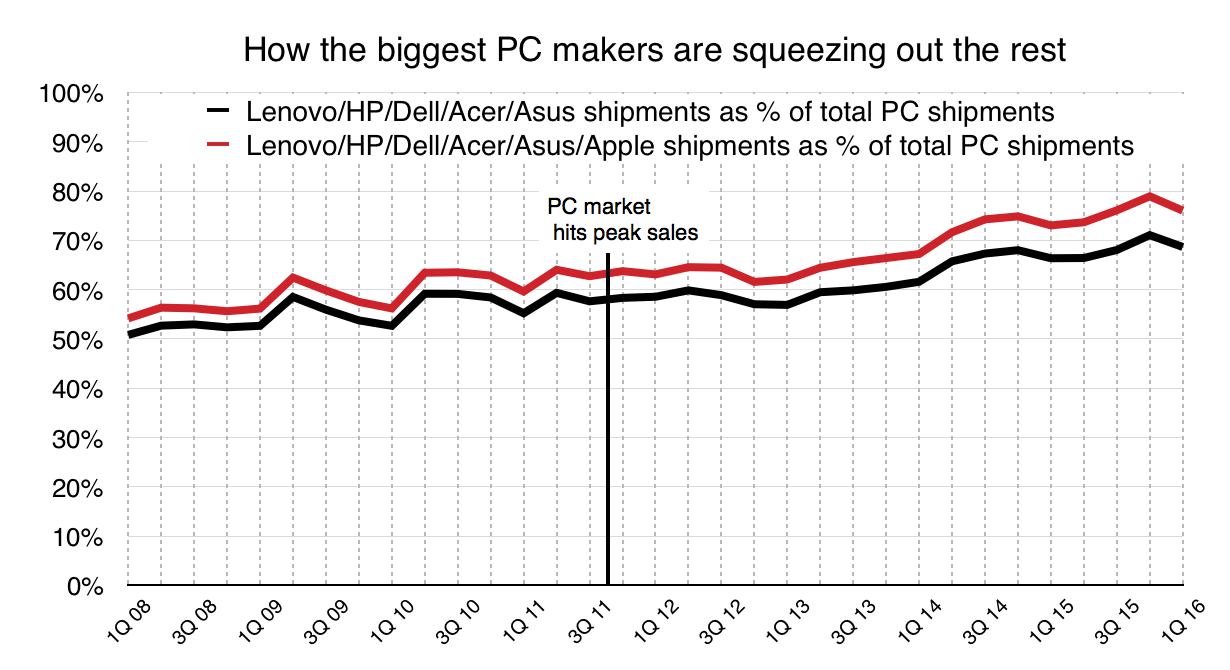
If you take “Other” to be companies such as Toshiba, Samsung, Fujitsu, and a myriad of others, then both their share and absolute number of shipments is going in a bad direction:
• Toshiba is struggling with an accounting scandal, and its PC shipments in the US fell by at least 25% in the first quarter, from 0.94m to less than 0.71m. The “Lifestyle” division, which includes the PC business, has seen revenues nearly halved since the calendar first quarter of 2014, and made an operating loss for the past 15 quarters.
• Samsung has withdrawn from Europe’s PC business and is hard to see elsewhere; its PC business is rolled into its IM division, which also includes its mobile division, for accounting. In Q4 2015 (the latest quarter for which there are figures) those revenues were US$780m – which would translate to 1m PCs sold at an ASP of $780, or more possibly 1.5m sold at an ASP of $520, or 2m at $390. (To make the top five for Q4 required shipment volumes of at least 5m.)
• For the fourth quarter, Fujitsu says revenues from PCs fell; it’s been saying that for at least a year.
There’s also a squeeze on Asian sub-scale PC makers, because the dollar’s strength hits them hard when they have to source components from the US (Microsoft Windows, perhaps?). That eats into profitability while the bigger players corner more of the market.
All this is going to lead to further consolidation. There’s already talk that Toshiba or Fujitsu will sell their PC businesses. Smaller companies might just shut up shop or seek a buyer.
Apple: Doing Fine, Thanks
Fourth, Apple is still solid. The USB-C Macbook is a year old and doesn’t show any sign of having set the PC world on fire but since the end of 2004 (a period stretching 46 quarters), Windows PCs have only seen faster than Apple growth in two quarters. Even while Apple’s total shipments (according to IDC and Gartner, ahead of Apple’s formal results later this month) fell in the most recent quarter, it was still nothing like the overall fall for Windows PC makers. Only Dell managed to stay upright better on the slippery slope, falling by 2.0% against Apple’s 2.1% (IDC); Gartner reckons Apple did better, showing 1.0% growth, but was bested by Asus with a 1.5% rise – perhaps through Windows tablet or convertible shipments.
What neither shows is that Apple commands the highest average prices in the industry. Once the figures for this quarter are in I’ll return to the topic but, for now, here are the figures for average selling prices (calculated from company financials and IDC shipment figures) for the big six PC companies:

As you can see, Apple is miles above the rest there. That also means it can grab a healthy profit, which allows it to stay in business when others struggle.
Conclusion
For the longer term? PCs are contracting towards a core base of users who really want or need them. If people want to be able to plug in USB sticks or SD cards, there’s a PC there for them. But it turns out that lots of people don’t and they’re voting with their wallets. That’s creating a squeeze on the smaller players, but even the big players don’t have it easy – unless, like Apple, they can charge a premium.

Is the decrease accounted for more by the installed base shrinking, or more by people buying new PC/Macs much less often (i.e., base is largely the same but average age of PC is increasing)? Also, is there evidence that young people (13-29) are not buying PC/Macs?