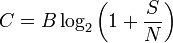By now, you’ve probably all heard or read about Apple’s new desktop operating system, Mac OS X 10.7 Lion, or just “Lion” for short. While I believe it is a really good operating system today, what I am most interested in is what it means for tomorrow. I’d like to share with you my thoughts on what I believe OSX Lion tells us about our computing future.

Device Modularity
Device modularity is essentially when one device, when docked or connected to another one, becomes something even better or more functional. It’s a world where a phone becomes a tablet; a tablet becomes a notebook and even a phone or tablet becomes a desktop. I’ve touched upon modularity with a few previous blogs covering the Motorola Atrix Lapdock and Multimedia Dock, the BlackBerry PlayBook and even the Motorola Xoom.
One of the inhibitors to good modularity is modality in UI. Or in other words, the smartphone, tablet, desktop, and laptop act like you would expect in the context you want. When you plug the phone into the dock to make it a laptop, it acts like a laptop, not a phone.
Lion has unified many of the UI elements and HCI (Human Computer Interface) between the iPhone, iPad, MacBook and the iMac:
· Gestures: Lion unifies gestures, or begins to, between the four platforms. Familiar gestures from iOS like pinch to zoom, tap to zoom, and swipe to navigate are just a few of the multi-platform gestures that are shared between phone, tablet, laptop, and desktop.

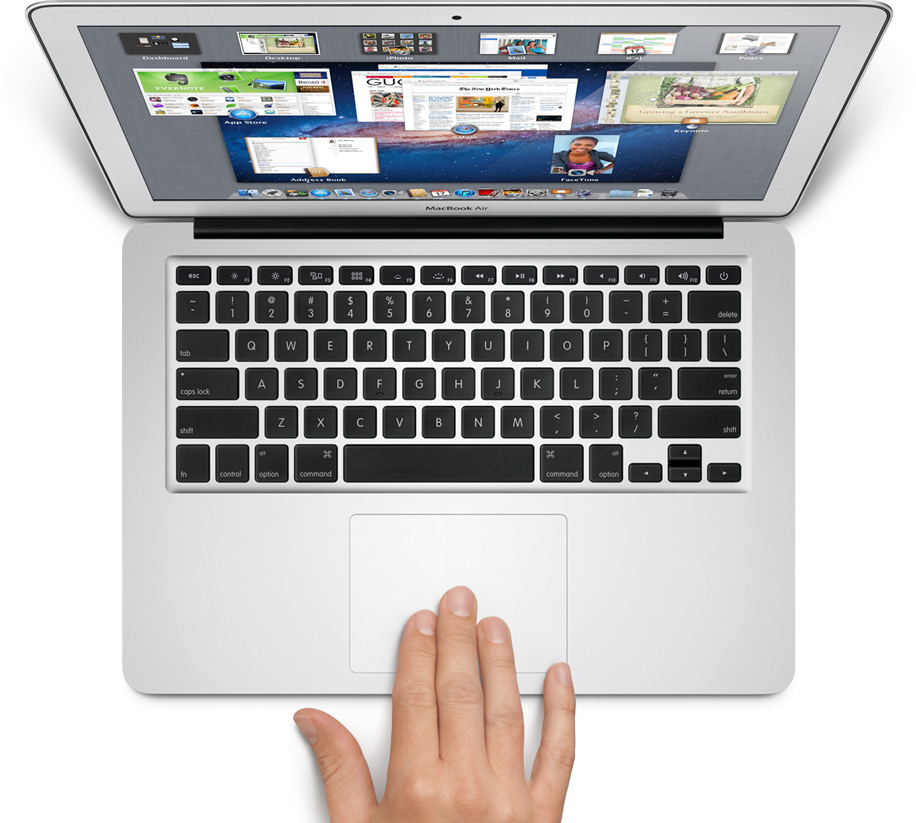
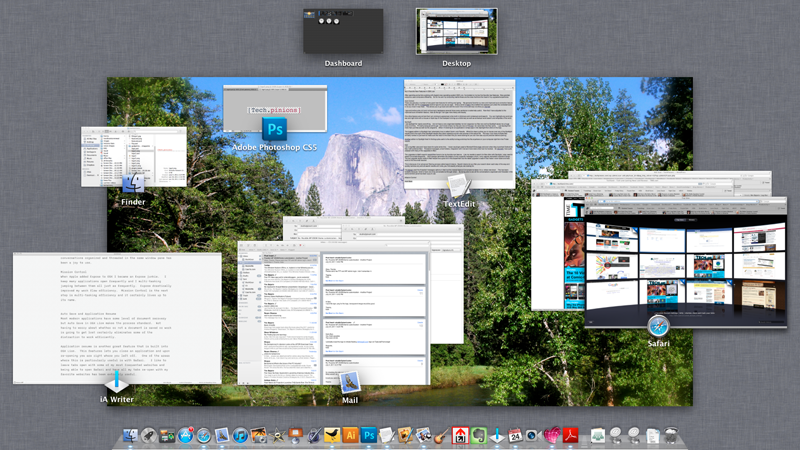
· Launchpad: Does this look familiar? This isn’t an iPad or iPhone; it’s Launchpad in Lion on a Mac Air laptop. Launchpad is a place for apps and folders of apps just like you see on the iPhone and iPad.

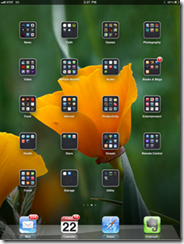
· Full screen apps: This isn’t exactly revolutionary if you’ve used Windows 7, but full screen apps does just that; allows apps to be maximized to the whole screen, just like iOS apps look with no windows. Then, a user can even “three finger swipe” between apps, similar to iOS 5.
So by unifying user interface and basic HCI, Lion has removed a major hurdle for the future, modular designs.
Air Gestures
We’ve all seen Microsoft Kinect in action in the living room and some of us have even seen “home-brew” tests using the Kinect SDK for the PC. Imagine more advanced, future computer “vision” on a much closer scale, or “near-field” basis, removing some of the actual physical peripherals. This could use very common and inexpensive cameras, possibly stereoscopic, with interconnects like CSI-3 and a heavy compute engine building a 3D model of the hand.
· “Magic Hand”: Consider removing the mouse and trackpad and replacing with a camera to use your own hand to do the gestures. Maybe even remove the keyboard and replace it with a projected virtual keyboard. The camera, like Kinect, tracks exactly what your hand is doing.

· Consistent Gestures: As described above, by having consistent gestures between all devices, the computer would be very focused on a specific set of near-field air gestures, not different ones by platform, increasing the chance of success.
With Lion unifying gestures today tied with future improvements with compute power and lower power with architectures like Fusion System Architecture, higher speed camera interconnects like CSI-3, a future without the physical mouse and trackpad becomes a distinct reality. Removing the physical keyboard is more of a stretch, but with pico projection a robust investment area, who knows? Also, with the success of keyboards on iOS and Android tablets, users are becoming conditioned to be satisfied with virtual, non-haptic keyboards.

Peer-to-Peer Communication
Peer-to-peer communications occur when one device directly interacts with another without the need for a LAN or WAN. The trend with services and the internet has led to the belief that peer-to-peer was dead. Not so with Lion, as it actually dialed it up a notch.
· Airdrop: Airdrop enables two Lion-based Macs to safely send files directly between each other without the need for an intermediate LAN or WAN. It automatically creates an ad-hoc WiFi-WiFi connection.
I find this very interesting given Apple’s forecast of a “post-PC” world. With very innovative features like HP’s “touch-to-share” and enabling communications like WiFi Direct and BlueTooth 4/5, peer-to-peer comms could be making a comeback. I’d guess that we will be seeing even more of this in CE devices. Who would have thought in this “everything in the cloud” world? J
Conclusion
OSX Lion is a really good operating system for users today and also gives us some indications of interesting things to come in the computing future. I believe that Lion tells us a lot about the future of device modularity, our ability to ditch the mouse, trackpad, and maybe even the keyboard. Lion also guides to a world that increases the likelihood of even more devices talking directly to each other without the cloud middleman. It’s a future I can get excited about. How about you?
Pat Moorhead is Corporate Vice President and Corporate Marketing Fellow and a Member of the Office of Strategy at AMD. His postings are his own opinions and may not represent AMD’s positions, strategies or opinions. Links to third party sites, and references to third party trademarks, are provided for convenience and illustrative purposes only. Unless explicitly stated, AMD is not responsible for the contents of such links, and no third party endorsement of AMD or any of its products is implied.
See Pat’s bio here or past blogs here.
Follow @PatrickMoorhead on Twitter and on Google+.
 The marriage of tech and media is definitely a rocky one at times, and Web TV is no exception. Despite all promises, like all relationships things are always evolving between tech and media – and sometimes they work, and sometimes they don’t. The latest tech / media couple in trouble appears to be Logitech and Google. With the rocky start to Google TV (the biggest player in Web TV so far), Logitech is also hung up in every way possible. Why? They supply the tech end of Google TV with the Revue Google TV set-top box.
The marriage of tech and media is definitely a rocky one at times, and Web TV is no exception. Despite all promises, like all relationships things are always evolving between tech and media – and sometimes they work, and sometimes they don’t. The latest tech / media couple in trouble appears to be Logitech and Google. With the rocky start to Google TV (the biggest player in Web TV so far), Logitech is also hung up in every way possible. Why? They supply the tech end of Google TV with the Revue Google TV set-top box. Market share is the moral of the story for both the data and the technology side of the equation right now. Any day now Google TV should be accessible by Android, and with 130 million users, that is a big deal. For now, Logitech has chosen to bite the revenue bullet and get more customers. That means a lower price in order to boost the real estate for Google.
Market share is the moral of the story for both the data and the technology side of the equation right now. Any day now Google TV should be accessible by Android, and with 130 million users, that is a big deal. For now, Logitech has chosen to bite the revenue bullet and get more customers. That means a lower price in order to boost the real estate for Google.