 Much of the initial reaction to the Apple v. Samsung trial was based more on emotion than critical thought in my opinion. The discussion over whether it is good or bad for consumers was interesting but again I felt mostly emotional. In all reality how is a challenge to uniquely innovate bad for anyone? As interesting as that element of the discussion was I thought the debate around design patents was a bit more interesting.
Much of the initial reaction to the Apple v. Samsung trial was based more on emotion than critical thought in my opinion. The discussion over whether it is good or bad for consumers was interesting but again I felt mostly emotional. In all reality how is a challenge to uniquely innovate bad for anyone? As interesting as that element of the discussion was I thought the debate around design patents was a bit more interesting.
As a part of our market analysis I keep a keen eye on what specific companies do to differentiate themselves in what I like to call the sea of sameness. To get a more holistic understanding on how differentiation may happen in the sea of sameness, I like to study how its done in other industries. Particularly ones that have been around for longer than the computer industry and also ones that are highly saturated and mature. We can make some interesting observation from industries like automotive and consumer packaged goods. It is observations from those industries that help us understand the importance of design patents and more importantly design consistency.
You Can’t Patent Rounded Corners
One of the least thought through elements of the whole trial was the part about rounded corners on specific products. In a post trial statement representatives from Samsung stated:
“It is unfortunate that patent law can be manipulated to give one company a monopoly over rectangles with rounded corners,”
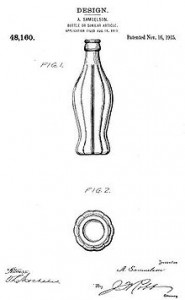
It seems as though there is a fundamental lack of understanding of the purpose of design patents. To explore this thought I think it would be helpful to look at a company with an interesting iconic design in Coca-Cola.
It is not just Coke’s logo which stands out but also the design of both their glass and plastic bottles. Coke owned a patent on the design of their glass bottle design in 1915 and the designs of their bottles have evolved but remained consistent in overall look and feel. It is this specific and unique design of the Coca-Cola bottle that helps it stand out in the sea of sameness.
If you went into a grocery store and looked at a wall of beverage containers, all without the labels, you can easily pick out the one which is a Coke bottle and that is the point. It is iconic, consistent, and easily identifiable.
Round Corners As a Design Philosophy
Now perhaps those engaging in the you can’t patent round corners debate have either no appreciation for consistent design philosophy or never taken a step back and looked at all of Apple’s products. Because when one does take a look at all of Apple’s products you will see that every piece of hardware follows the four perfectly asymmetrical rounded corners design.
This design philosophy has been in place for quite some time. One could argue that the rounded corners on a screen started with the first colored iMac’s. From that point on the four asymmetrical rounded corners began to become a consistent theme of all Apple hardware.

The goal again of these “rounded corners” is to maintain a unique, consistent, iconic, and easily identifiable Apple product. To carry on my point about the Coke Bottle, if you were to look at a table full of notebooks, all without logos, Picking out the one that is Apple’s would be easy. This is not something I can confidently say with regards to any other PC OEM with the exception of Lenovo.
Most other vendors who make hardware change their design theme from year to year based on what the trends are. Because of that often they change so drastically from year to year that is it clear no overall design theme is being employed. In fact I would contend that for the average consumer no designed personal computer hardware is more easily identified than Apple’s.
This is true in the smart phone and tablet space as well. That I feel is what Apple was trying to protect with their claims that Samsung’s 10.1 tablet had corners that were rounded identically to the corners on all other Apple products. Apple is deploying a design philosophy that is consistent and intentional. Samsung, with regards to tablets, is not, and that was the point.
Understanding the design philosophy from Apple becomes interesting as we think about future products. The only reason you would defend a design philosophy or design patent for that matter, is if you intend to stick to it for the foreseeable future.
This is clearly one way Apple intends to help its products stand out in the sea of sameness–at least from a design perspective. Sticking to this design philosophy and maintaining the consistency of size, shape, and colors, will continue to make Apple’s products not only be objects of desire but also easily recognized year after year by consumers. Which is all part of the strategy.
